Mango Safety Inspection
Detect Calcium Carbide artificial ripening in mangoes
Inspection Guide
Click to enlarge
How to Inspect Mangoes
Mangoes are frequently ripened using Calcium Carbide, which contains arsenic and phosphorus impurities.
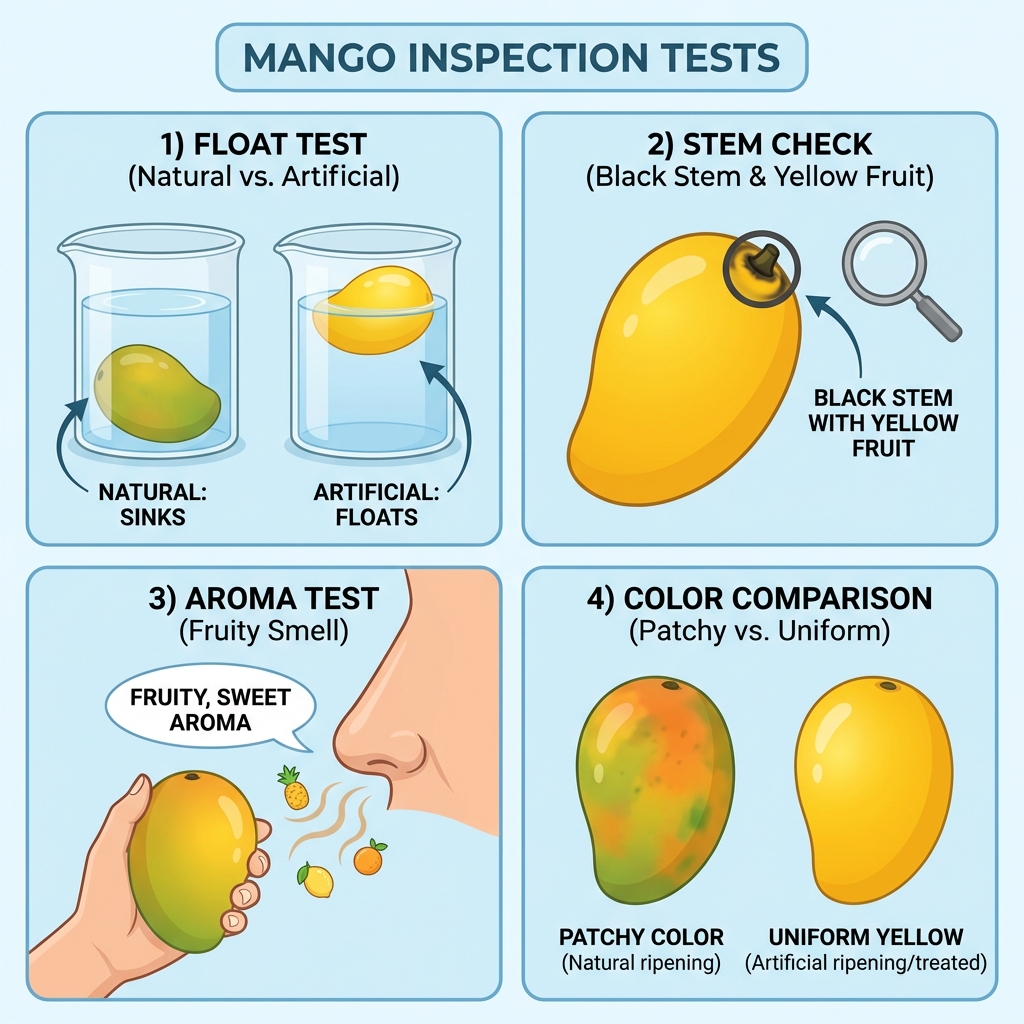
1. The Float Test:
Naturally ripened mangoes usually sink or stay submerged in water because of their higher sugar density. Carbide-ripened mangoes often float on the surface.
2. Stem Appearance:
If the stem-end is black but the fruit is bright yellow, it indicates chemical stress from carbide treatment.
3. The Aroma Test:
Natural mangoes have a strong, sweet scent at the stem. Artificially ripened ones often have a faint chemical smell or no smell at all.
4. The Smell Intensity Test:
Natural mangoes have progressively stronger aroma as they ripen. Carbide-ripened mangoes either have very faint aroma or none at all, even when soft.
5. Visual Color Check:
Look for patchy coloring with bright yellow and green spots together - a sign of uneven artificial ripening.
Quick Safety Tips
- Perform float test - natural mangoes sink
- Check stem color - black indicates chemicals
- Smell test - strong aroma indicates natural ripening
- Soak in water for 30 minutes before consumption
Chemical Concerns
Step 1: AI Visual Scan
New to BioLens? Try a sample test
