Moong Dal (Green Gram) Safety Inspection
Detect Kesari dal and artificial yellow dye in Moong Dal
Inspection Guide
Click to enlarge
Moong Dal Purity Detection
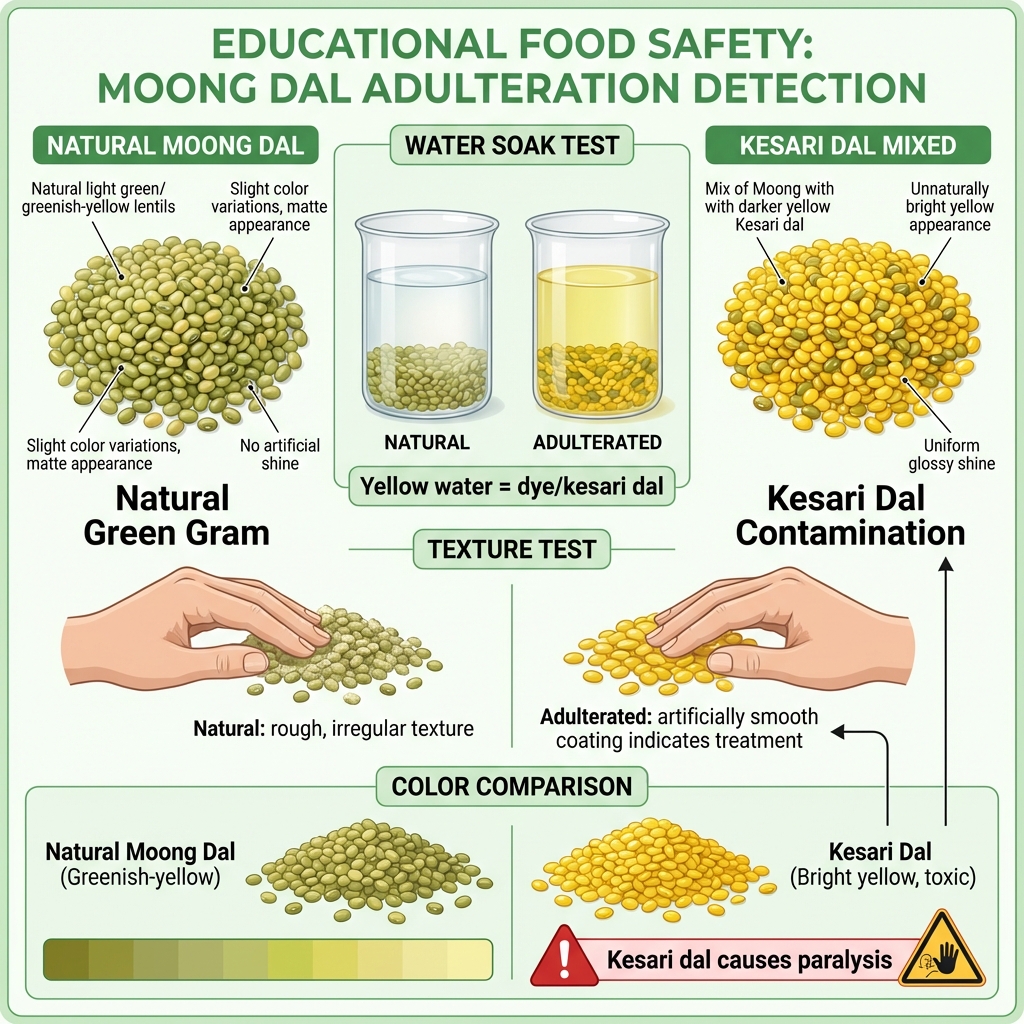
Moong Dal is frequently adulterated with Kesari dal and artificial yellow coloring agents to enhance appearance and reduce costs.
1. The Split Shape Test:
Natural Moong dal (split green gram) has a characteristic oval shape with one flat side (where it was split). Kesari dal is similar but slightly more angular and irregularly shaped. Look for consistency in shape.
2. The Color Uniformity Check:
Pure Moong dal has a natural pale yellow to greenish-yellow color with slight variations between grains. If all grains are uniformly bright yellow with no variation, artificial coloring is likely present.
3. The Water Soaking Test:
Soak dal in water for 2-3 hours. Natural Moong dal will absorb water and swell, with minimal color leaching. If the water turns distinctly yellow or the dal releases excessive color, it indicates dye presence or Kesari dal mixing.
4. The Cooking Color Test:
Cook a small portion. Natural Moong dal becomes soft yellow when cooked. If the dal retains an unnaturally bright yellow color after cooking or if some dal pieces remain hard while others are soft (indicating mixed varieties), it's adulterated.
5. The Surface Texture Test:
Examine the dal surface closely. Natural Moong dal has a smooth but not glossy surface. If the surface appears too shiny or has a powdery coating, it may have been treated with color or polish.
Quick Safety Tips
- Check for natural pale yellow-green color with variations
- Soak in water and observe for color leaching
- Look for consistent oval split shape
- Cook test - natural dal softens uniformly
Chemical Concerns
Step 1: AI Visual Scan
New to BioLens? Try a sample test
